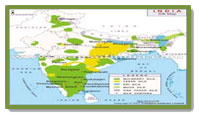
OUR IMPACT
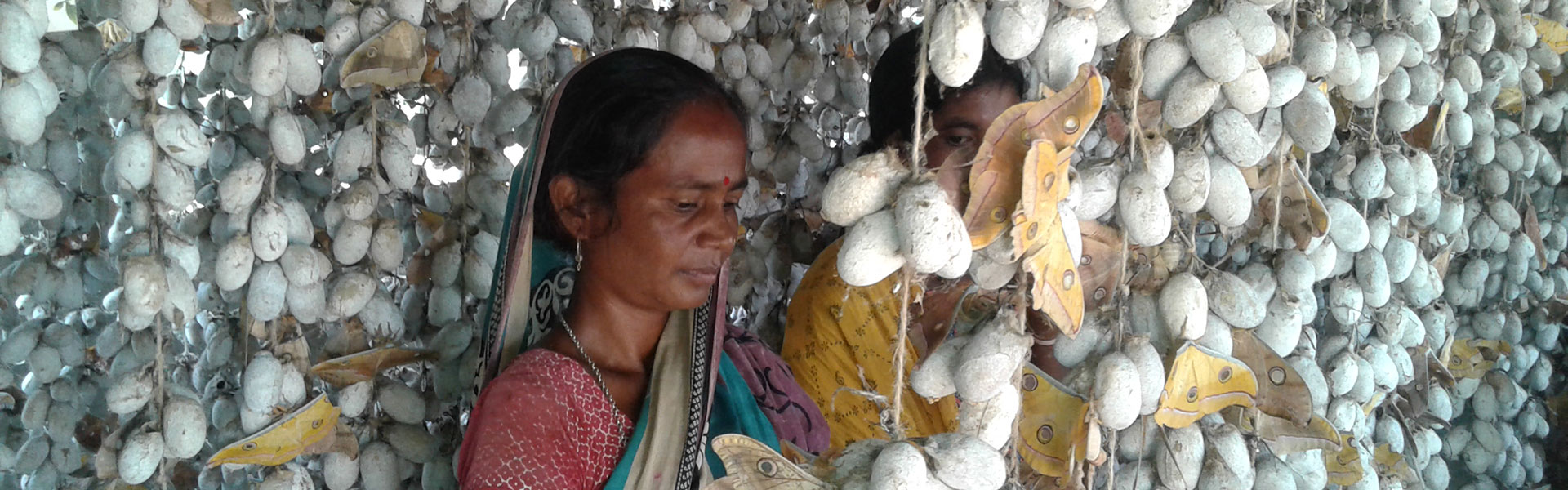
From a fragile forest-based income activity, Tasar has emerged as a robust livelihood options
Proven competitive advantage in utilizing slack labor and idle assets of families.
Inclusion of poor in the overall value chain, involvement of women increased significantly,
The sector has been able to attract and retain young people,
Income sustainability.